2018 News & Events
TOAR: China is Hot Spot of Ground-Level Ozone Pollution
29 August 2018
adapted slightly from the story by CIRES Communications

Ozone levels are higher across China than in other countries tracking the air pollutant.
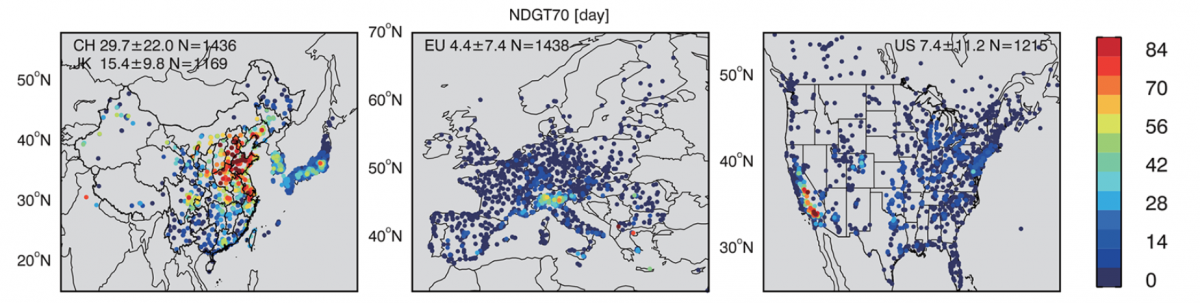
In China, people breathe air thick with the lung-damaging pollutant ozone two to six times more often than people in the United States, Europe, Japan, or South Korea, according to a new assessment. By one metric – total number of days with daily maximum average ozone values (8-hour average) greater than 70 ppb – China had twice as many high ozone days as Japan and South Korea, three times more than the United States, and six times more than Europe.
"We find that in the most populous urban regions of Eastern and Central China, there are more than 60 days in a calendar year with surface ozone levels exceeding the Chinese national ozone air quality standard," said Lin Zhang of Peking University, lead author of the study in the current issue of Environmental Science & Technology Letters.
"China has become a hot spot of present-day surface ozone pollution," said Owen Cooper, a co-author on the research paper and a CIRES scientist working at CSD. "Human and vegetation exposure in China is greater than in other developed regions of the world with comprehensive ozone monitoring."
Many countries regulate ozone because of the damage the pollutant does to plants and people.
In the United States, for example, the current health-based standard for ground-level ozone, set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, is 70 ppb (based on the maximum daily 8-hour average). The Chinese national ozone air quality standard is a daily maximum 8-hour average greater than 160 micrograms per cubic meter, equivalent to about 80 ppb.
Ground level ozone is most commonly formed when volatile organic compounds and nitrogen oxides react in the atmosphere in the presence of sunlight. The burning of fossil fuels and biomass burning (from crop clearing or forest fires) are major sources of volatile organic compounds and nitrogen oxides. Since the 1990s, tighter controls on emissions of those ingredients have lessened ozone pollution in many European and U.S. cities. But the extent of surface ozone pollution in China hasn't been widely recognized, in part because there were so few Chinese monitoring sites before 2012, according to the researchers.
For this study, the researchers used data from a relatively new network of 1,600 ozone monitors in China and a massive new global ozone database to quantify ozone levels in China and compare those to the levels in other countries.
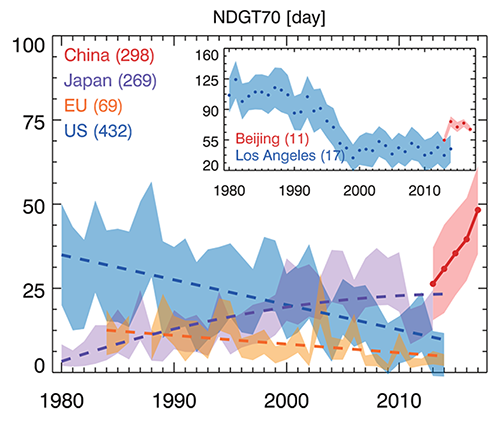
The new report shows that China has higher ozone pollution levels than all nations with ozone monitors, including the United States, Europe, Japan, and South Korea. Every ozone metric the researchers looked at rose continuously in China over the last five years. "We found the largest increases in ozone exposure in eastern and central China, especially in the most populous areas. These results indicate an increasing severity of human and crop/ecosystem ozone exposure across China," said Xiao Lu in Zhang's group, first author of the study.
In fact, present-day ozone levels in major Chinese cities are comparable to U.S. levels in the 1980s and 1990s. "Ozone levels in Beijing today are similar to Los Angeles in the 1990s, when emission controls were just beginning to have an impact on reducing ozone levels there," said Cooper.
Winter vs. Summer Challenges
For the past several years, wintertime haze pollution has been the main public concern in China and the focus of government action on air pollution, according to Zhang. The Chinese government has implemented stringent emission control measures to improve air quality: Since 2013, the Action Plan on Air Pollution Prevention and Control has reduced the concentration of primary air pollutants and particulate matter an average of 35 percent for 74 major cities.
Zhang and Lu think the harmful effects of surface ozone pollution are much less recognized. "Many people in China do not realize that we may suffer severe ozone pollution under a typical blue sky in summer days. The emerging severity of ozone pollution in China now presents a new challenge for emission control strategies," Zhang said.
Ozone Harms Crops
Because ozone can harm plants, including crops, the researchers also investigated the potential for ozone-induced plant damage in China. One vegetation metric they examined captures accumulated ozone exposure exceeding a threshold above which tree growth or crop yield is expected to be reduced, over a crop's typical three-month growing season.
In China, values for that metric were 1.4 to 2 times higher than in Japan, South Korea, Europe, and the United States. Studies done before 2010 at a few Chinese sites concluded that ozone pollution was already reducing wheat yields up to 6 to 15 percent. "And because ozone levels in China have increased since then, we would expect to see even greater crop loss now," said Cooper.
Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report
The database the researchers used in this analysis is part of the Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report (TOAR), a series of global assessments of ozone pollution and its relevance to people, plants, and climate. Owen Cooper is chair of the research project's steering committee. "This is exactly the kind of follow-on assessment we hoped TOAR would inspire," he said. According to lead author Zhang, scientists have known that there are high surface ozone levels in present-day China; what they didn't know was how China's ozone pollution compared with other industrialized countries in terms of magnitude, frequency, human, and vegetation exposure. "Our study presents such a novel comparison by combining the Chinese ozone data with the TOAR dataset," said Zhang.
Lu, X., J. Hong, L. Zhang, O.R. Cooper, M.G. Schultz, X. Xu, T. Wang, M. Gao, Y. Zhao, and Y. Zhang, Severe surface ozone pollution in China: A global perspective, Environmental Science & Technology Letters, doi:10.1021/acs.estlett.8b00366, 2018.
Abstract
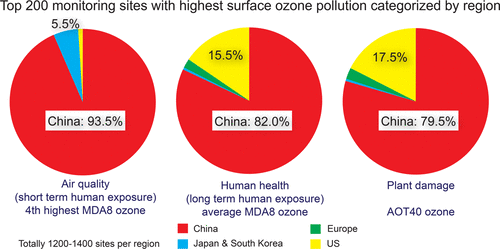
The nationwide extent of surface ozone pollution in China and its comparison to the global ozone distribution have not been recognized because of the scarcity of Chinese monitoring sites before 2012. Here we address this issue by using the latest 5 year (2013-2017) surface ozone measurements from the Chinese monitoring network, combined with the recent Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report (TOAR) database for other industrialized regions such as Japan, South Korea, Europe, and the United States (JKEU). We use various human health and vegetation exposure metrics. We find that although the median ozone values are comparable between Chinese and JKEU cities, the magnitude and frequency of high-ozone events are much larger in China. The national warm-season (April-September) fourth highest daily maximum 8 h average (4MDA8) ozone level (86.0 ppb) and the number of days with MDA8 values of >70 ppb (NDGT70, 29.7 days) in China are 6.3-30% (range of regional mean differences) and 93-575% higher, respectively, than the JKEU regional averages. Health exposure metrics such as warm-season mean MDA8 and annual SOMO35 (sum of ozone means over 35 ppb) are 6.3-16 and 25-95% higher in China, respectively. We also find an increase in the surface ozone level over China in 2016 and 2017 relative to 2013 and 2014. Our results show that on the regional scale the exposure of humans and vegetation to ozone is greater in China than in other developed regions of the world with comprehensive ozone monitoring.